[LeetCode January Challange] Day 2 - Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree
Given two binary trees original and cloned and given a reference to a node target in the original tree.
The cloned tree is a copy of the original tree.
Return a reference to the same node in the cloned tree.
Note that you are not allowed to change any of the two trees or the target node and the answer must be a reference to a node in the cloned tree.
Follow up: Solve the problem if repeated values on the tree are allowed.
Example 1:
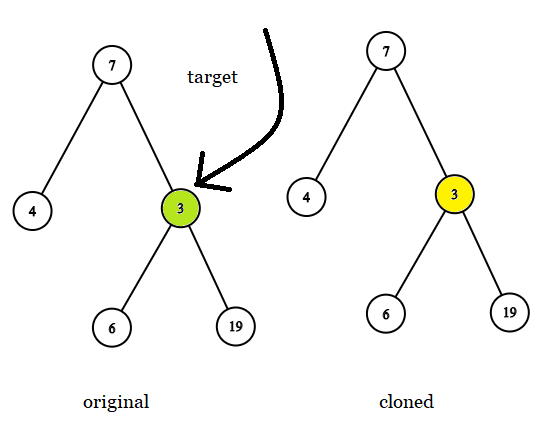
Input: tree = [7,4,3,null,null,6,19], target = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: In all examples the original and cloned trees are shown. The target node is a green node from the original tree. The answer is the yellow node from the cloned tree.
Example 2:

Input: tree = [7], target = 7
Output: 7
Example 3:
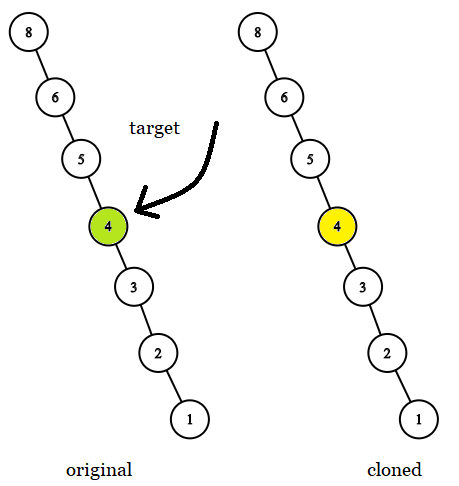
Input: tree = [8,null,6,null,5,null,4,null,3,null,2,null,1], target = 4
Output: 4
Example 4:
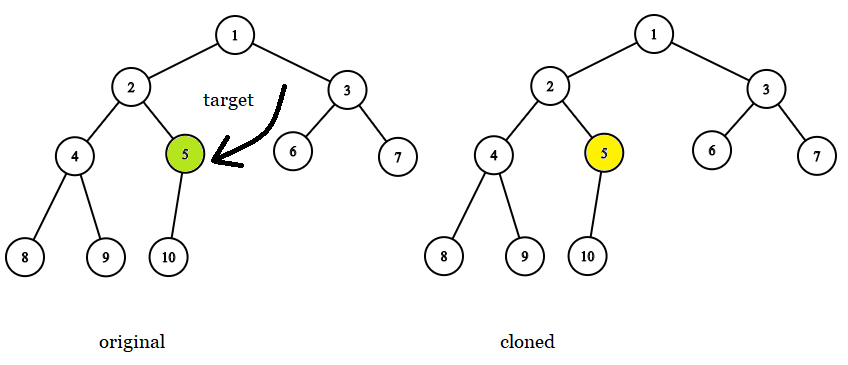
Input: tree = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], target = 5
Output: 5
Example 5:
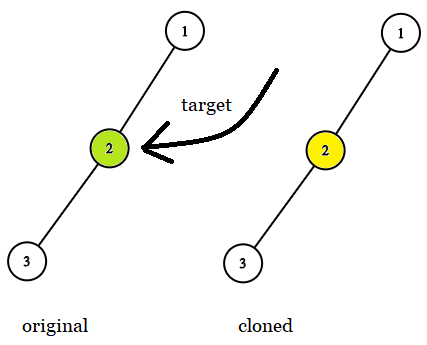
Input: tree = [1,2,null,3], target = 2
Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 10^4].
- The values of the nodes of the tree are unique.
- target node is a node from the original tree and is not null.
Solution
Time complexity : O(n)
Space complexity : O(h)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* getTargetCopy(TreeNode* original, TreeNode* cloned, TreeNode* target) {
if (original == target) return cloned;
if (!original) return nullptr;
if (TreeNode* left = getTargetCopy(original->left, cloned->left, target))
return left;
return getTargetCopy(original->right, cloned->right, target);
}
};
使用DFS,兩邊同時移動,origin 找到的同時,clone 端即是所求。