[LeetCode March Challange] Day 09 - Add One Row to Tree
Given the root of a binary tree and two integers val and depth, add a row of nodes with value val at the given depth depth.
Note that the root node is at depth 1.
The adding rule is:
- Given the integer depth, for each not null tree node cur at the depth depth - 1, create two tree nodes with value val as cur’s left subtree root and right subtree root.
- cur’s original left subtree should be the left subtree of the new left subtree root.
- cur’s original right subtree should be the right subtree of the new right subtree root.
- If depth == 1 that means there is no depth depth - 1 at all, then create a tree node with value val as the new root of the whole original tree, and the original tree is the new root’s left subtree.
Example 1:
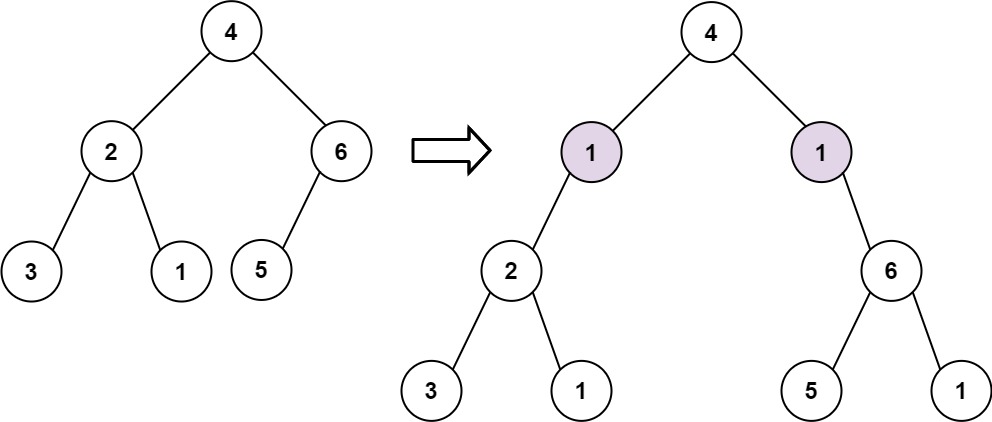
Input: root = [4,2,6,3,1,5], val = 1, depth = 2
Output: [4,1,1,2,null,null,6,3,1,5]
Example 2:
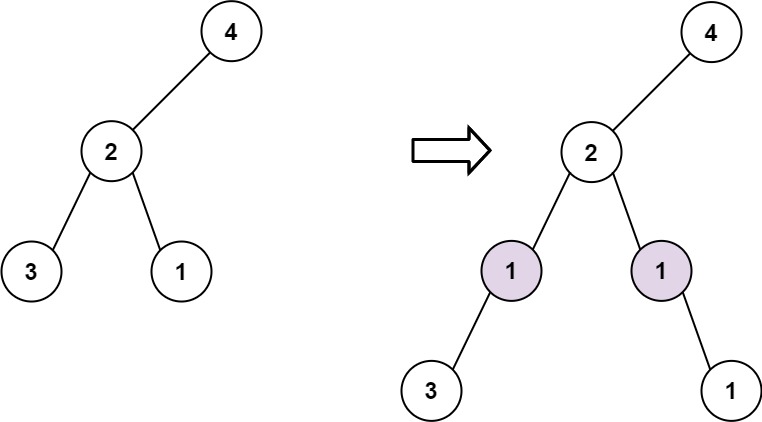
Input: root = [4,2,null,3,1], val = 1, depth = 3
Output: [4,2,null,1,1,3,null,null,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 10^4].
- The depth of the tree is in the range [1, 10^4].
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
- -10^5 <= val <= 10^5
- 1 <= depth <= the depth of tree + 1
Solution
BFS
Time complexity : O(n)
Space complexity : O(logn)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int val, int depth) {
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
else if (depth == 1) return new TreeNode(val, root, nullptr);
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
int cur_d = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
++cur_d;
queue<TreeNode*> next_q;
while (!q.empty()) {
TreeNode* cur = q.front(); q.pop();
if (cur_d == depth-1) {
cur->left = new TreeNode(val, cur->left, nullptr);
cur->right = new TreeNode(val, nullptr, cur->right);
}
if (cur->left) next_q.push(cur->left);
if (cur->right) next_q.push(cur->right);
}
if (cur_d == depth) break;
q = next_q;
}
return root;
}
};
Recusion
Time complexity : O(n)
Space complexity : O(n)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* addOneRow(TreeNode* root, int val, int depth) {
if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;
if (depth == 1) return new TreeNode(val, root, nullptr);
if (depth == 2) {
root->left = new TreeNode(val, root->left, nullptr);
root->right = new TreeNode(val, nullptr, root->right);
} else {
addOneRow(root->left, val, depth-1);
addOneRow(root->right, val, depth-1);
}
return root;
}
};