[LeetCode December Challange] Day 3 - Increasing Order Search Tree
Given the root of a binary search tree, rearrange the tree in in-order so that the leftmost node in the tree is now the root of the tree, and every node has no left child and only one right child.
Example 1:
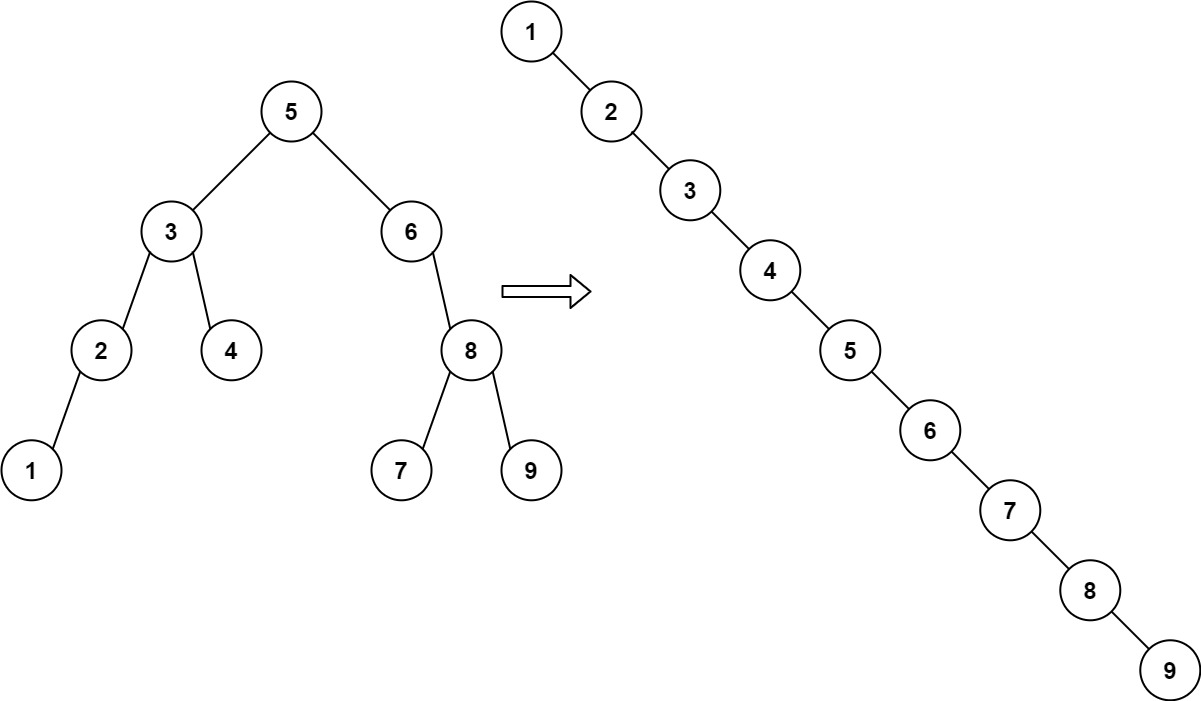
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,8,1,null,null,null,7,9]
Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6,null,7,null,8,null,9]
Example 2:

Input: root = [5,1,7]
Output: [1,null,5,null,7]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be in the range [1, 100].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution
Time complexity : O(n)
Space complexity : O(h)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* increasingBST(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode dummy_head = TreeNode(0);
cur = &dummy_head;
inorder(root);
return dummy_head.right;
}
void inorder(TreeNode* node) {
if (!node) return;
inorder(node->left);
node->left = nullptr;
cur->right = node;
cur = node;
inorder(node->right);
}
private:
TreeNode* cur;
};
創一個新的 dummy head ,因在 BST 上 inorder traverse 後的結果會是由小到大的結果,故以 inorder 的處理順序,依序把左子樹拿掉,連到 dummy head 那邊,更新目前尾巴的位置,即可。