[LeetCode August Challange]Day7-Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1) and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
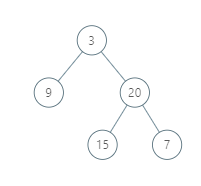
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:

Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and 1000 nodes.
- Each node’s value will be between 0 and 1000.
solution
Time complexity : O(nlogn)
Space complexity : O(n)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
x_min_ = INT_MAX;
x_max_ = INT_MIN;
inorderTraversal(root, 0, 0);
vector<vector<int>> res(x_max_-x_min_+1);
for (auto it: map_) {it.first.second);
int x = it.first.second - x_min_;
res[x].insert(end(res[x]), begin(it.second), end(it.second));
}
return res;
}
private:
map<pair<int, int>, set<int>> map_;
int x_min_, x_max_;
void inorderTraversal(TreeNode* node, int x, int y) {
if (!node) return;
x_min_ = min(x_min_, x);
x_max_ = max(x_max_, x);
map_[{y, x}].insert(node->val);
inorderTraversal(node->left, x-1, y+1);
inorderTraversal(node->right, x+1, y+1);
}
};
用pair (y, x) map to int set。
在traverse時的y與題目相反,用增加的,可以讓map以y優先小到大放置(即樹的上到下),將traverse結果一一存入map中,同時記錄x值的最小、最大值,以便求範圍。
再根據x值的範圍,建出res array,再把map中的元素一一放入res中。