[LeetCode February Challange] Day 9 - Convert BST to Greater Tree
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), convert it to a Greater Tree such that every key of the original BST is changed to the original key plus sum of all keys greater than the original key in BST.
As a reminder, a binary search tree is a tree that satisfies these constraints:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Note: This question is the same as 1038:
Example 1:
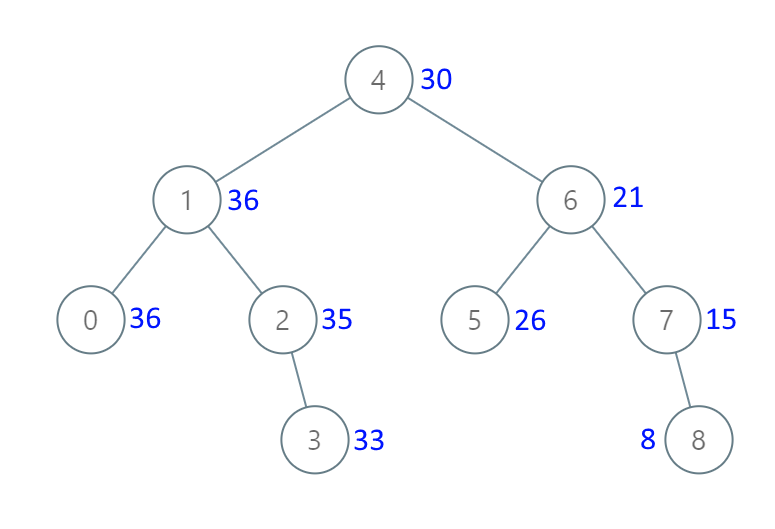
Input: root = [4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
Output: [30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
Example 2:
Input: root = [0,null,1]
Output: [1,null,1]
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,0,2]
Output: [3,3,2]
Example 4:
Input: root = [3,2,4,1]
Output: [7,9,4,10]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 10^4].
- -10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4
- All the values in the tree are unique.
- root is guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
Solution
Time complexity : O(n)
Space complexity : O(n)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* convertBST(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root, 0);
return root;
}
private:
int dfs(TreeNode* node, int acc) {
if (node == nullptr) return acc;
acc = dfs(node->right, acc);
node->val += acc;
acc = dfs(node->left, node->val);
return acc;
}
};
用 dfs 右中左的方式去遍歷整棵樹,以一個 node 的觀點來看:
- 將目前 acc 值往右子樹傳,並更新 acc 值。
- 此時 acc 為比此 node 還要大的值的總和,更新此 node 值。
- 將目前 acc 值(即更新後的此 node 值)往左子樹傳,並更新 acc 值。
- 回傳 acc 值給 parent node。