[LeetCode October Challange] Day 31 - Recover Binary Search Tree
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Follow up: A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight forward. Could you devise a constant space solution?
Example 1:
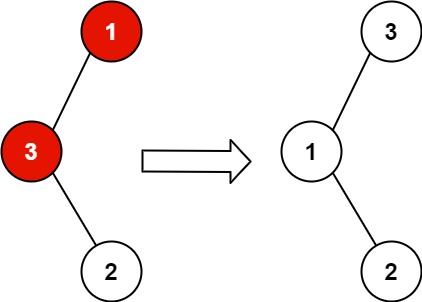
Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2]
Output: [3,1,null,null,2]
Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Example 2:

Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2]
Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3]
Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [2, 1000].
- -2^31 <= Node.val <= 2^31 - 1
Solution
Time complexity : O(n)
Space complexity : O(n)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void recoverTree(TreeNode* root) {
prev = first = second = nullptr;
inorder(root);
swap(first->val, second->val);
}
void inorder(TreeNode* node) {
if (!node) return;
inorder(node->left);
if (prev && prev->val > node->val) {
second = node;
if (!first) first = prev;
}
prev = node;
inorder(node->right);
}
private:
TreeNode *prev, *first, *second;
};
根據Binary Search Tree,在inorder traversal後會是已排序的性質下來做。
就找到prev比當前node大的做記錄。
跑完一輪inorder traversal後,找到兩個該交換的點,將其值交換即可。