[LeetCode October Challange] Day 13 - Sort List
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in O(n logn) time and O(1) memory (i.e. constant space)?
Example 1:
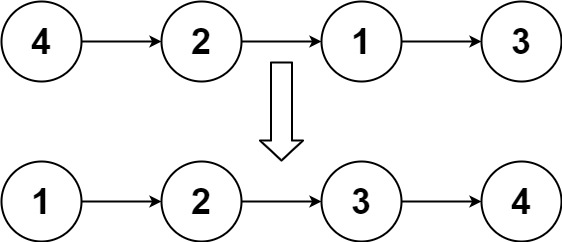
Input: head = [4,2,1,3]
Output: [1,2,3,4]
Example 2:

Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 5 * 104].
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
Solution
Top-Down link-list merge sort.
Time complexity : O(n log(n))
Space complexity : O(log(n))
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head->next;
while (fast && fast->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode *second_head = slow->next;
slow->next = nullptr;
return merge(sortList(head), sortList(second_head));
}
private:
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode dummy = ListNode(0);
ListNode* tail = &dummy;
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1->val > l2->val) swap(l1, l2);
tail->next = l1;
tail = tail->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
tail->next = l1 ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}
};
先不斷的一分為二,再兩兩合併。
slow指標每次走一步,fast指標每次走二步,可用此法找出中間點。
合併時,不斷找兩list中最小值,當作下一個節點。
Bottom-Up link-list merge sort.
Time complexity : O(n log(n))
Space complexity : O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
int len = 0;
for (ListNode* cur=head; cur!=nullptr; cur=cur->next)
++len;
ListNode dummy(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode* tail;
ListNode *l, *r, *rest;
for (int n=1; n<len; n<<=1) {
rest = dummy.next;
tail = &dummy;
while (rest) {
l = rest;
r = split(l, n);
rest = split(r, n);
auto merged = merge(l, r);
tail->next = merged.first;
tail = merged.second;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
private:
ListNode* split(ListNode* head, int n) {
while (head && --n)
head = head->next;
ListNode *next_start = head ? head->next : nullptr;
if (head) head->next = nullptr;
return next_start;
}
pair<ListNode*, ListNode*> merge(ListNode* l, ListNode* r) {
ListNode dummy(0);
ListNode* tail = &dummy;
while (l && r) {
if (l->val > r->val) swap(l, r);
tail->next = l;
tail = tail->next;
l = l->next;
}
if (l) tail->next = l;
if (r) tail->next = r;
while (tail->next) tail = tail->next;
return {dummy.next, tail};
}
};
相較於Top-Down,Bottom-Up沒有不斷的從中點切,而是直接將原list視為已切分好的list,2個一組、4個一組、8個一組、…往上合併。
無需遞迴、而且操作上是in-place。